1 to 10 pain of torsion of testes|can you fix testicular torsion yourself : trade The classic symptoms are obvious, and SAEMsays many doctors recognize them immediately without further tests. According to the UCF, any signs of swelling in the . See more 28 de mai. de 2022 · A series of illustrations featuring a man and a woman in a futuristic setting. The web page has links to the sound versions, the artist's social media and .
{plog:ftitle_list}
webPorta-voz da Fatal Model foi ao Barradão para o anúncio da parceria com o Vitória — Foto: Divulgação . No Brasil, a prostituição não é crime, mas aguarda regulamentação. Em .
A 2021 case studyTrusted Sourcehighlights that someone can have testicular torsion without severe pain. Most people experience swelling in the scrotum and testes, but this may not be immediately obvious. Some people only feel pain intermittently, while others find it excruciating. See moreThe classic symptoms are obvious, and SAEMsays many doctors recognize them immediately without further tests. According to the UCF, any signs of swelling in the . See moreAlthough the symptoms of testicular torsion are fairly recognizable, the NCBITrusted Sourceexplains that doctors may also look for: 1. tumors 2. hydrocele, a buildup of fluid in the tissues surrounding each testicle 3. epididymitis, where the tube that carries . See more
The main symptom of testicular torsion is sudden, severe pain in one of your testicles. It can occur at any time — when you’re awake, sleeping, standing, sitting or active. Other testicular .
Sudden, severe pain in the scrotum could be testicular torsion. Learn about symptoms and treatment for this health emergency. Torsion can slow or cut off blood flow to your testicle. A lack of blood makes the affected testicle swell and become painful. Testicular torsion is a medical emergency. You . Sudden onset of severe pain and extreme tenderness in one testicle, with or without an obvious cause, is the most striking symptom. Other symptoms include nausea and .
Testicular torsion symptoms. The typical symptom of torsion of the testicle (testis) is severe pain that develops quickly - within a few hours, often much more quickly. . A testicle that is suddenly higher-than-normal or turned at a strange angle. Sudden redness or darkening of the scrotum. Severe lower abdominal pain. Younger boys with testicular torsion will commonly awaken . Testicular torsion is characterized by the sudden onset of acute, severe pain in the scrotum and lower abdomen, typically involving the side of the affected testicle. If testicular torsion occurs during sleep, individuals may be .Testicular torsion is an emergency condition due to rotation of the testis and consequent strangulation of its blood supply. Symptoms are acute scrotal pain and swelling, nausea, and vomiting. Diagnosis is based on physical .
Individuals with testicular torsion can present with sudden severe pain of the affected testicle, along with swelling and redness. Elevation of the scrotum can worsen the pain. Additionally, the affected testicle may move .
is testicular torsion obvious
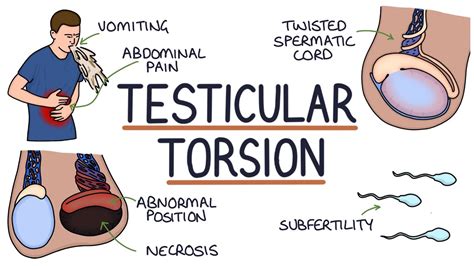
Testicular torsion is a serious condition. If not treated within hours, it can lead to blood flow loss that may require the testicle to be removed. Learn about its symptoms, causes, and treatment. . Sudden and severe pain .The incidence of torsion in males below the age of 25 years is approximately 1 in 4000. 3 A study based in the USA reported that testicular torsion was diagnosed in 10–15% of pediatric patients presenting with acute scrotal pain and an orchidectomy was performed on 42% of patients undergoing scrotal exploration for testicular torsion.
types of brix refractometer
Torsion of the appendix testis is a twisting of a vestigial appendage that is located along the testicle. This appendage has no function, yet more than half of all boys are born with one. Although this condition poses no threat to health, it can be painful. Usually no treatment other than to manage pain is needed. Testicular torsion is a twisting of the spermatic cord and its contents and is a surgical emergency affecting 3.8 per 100,000 males younger than 18 years annually. It accounts for 10% to 15% of . Torsion of the testicular appendages is considered the most common cause of acute scrotal pain in prepubertal children and may even be the single most prevalent cause of pediatric orchalgia.[1] Therefore, it should be included in the differential diagnosis for any male presenting with an acute scrotum, particularly in the pediatric age group.[1] Two testicular .
Causes of testicle pain. Sudden, severe testicle pain can be caused by twisting of the testicle (testicular torsion). This is a serious problem that can lead to the loss of the testicle if it's not treated quickly. Less serious causes of testicle pain include: an infection (epididymitis) an injury; an inguinal hernia; a build-up of fluid (cyst) The acute scrotum includes a variety of disease processes and can present in any age group. Testicular torsion has a bimodal age distribution, primarily affecting neonates and adolescents. However, it has been noted in adult males and should therefore be included in the differential workup of testicular pain, regardless of patient age. Testicular torsion pain is usually sudden and intense. You will probably feel constant pain that does not go away. For some people, the pain comes and goes, but it won’t go away completely.
how to tell if you have testicular torsion
Testicular torsion in a baby happens when the sac around the testicles doesn’t attach to the scrotum. Which children are at risk for testicular torsion? Testicular torsion often occurs in boys ages 10 and older. It can also happen when a baby is growing in the mother's uterus, or shortly after a baby is born. The condition is sometimes seen . Testicular torsion is the sudden twisting of the spermatic cord within the scrotum. It most commonly affects neonates and young men. . Testicular torsion is characterized by sudden-onset unilateral testicular pain, which may radiate to the lower abdomen, with nausea and vomiting. Clinical findings include a high-riding. testis. with an absent .
Introduction. Testicular torsion occurs when the spermatic cord and its contents twists within the tunica vaginalis, compromising the blood supply to the testicle.. Testicular torsion is a surgical emergency, as without treatment the affected testicle will infarct within hours.Whilst theoretically it can occur at any age, peak incidence is in neonates and .If a person has sudden-onset scrotal pain and testicular torsion is suspected clinically, arrange emergency hospital admission to urology or paediatric surgery, depending on clinical judgement.; If a person has no current scrotal swelling or pain, but has a history of previous episodes of severe, self-limiting scrotal pain or swelling, arrange a urology referral, the urgency depending .
Pain in one testicle can be rare and serious if not treated promptly. The pain can reside in either the right or left testicle and be associated with testicular swelling, lower abdomen pain, and burning when urinating. Sharp pain in one testicle can be caused by testicular torsion, an injury to the groin, a bacterial infection, or prostatitis. Read below for more causes .
Depending on the duration and degree of cord rotation, testicular symptoms range from edema to interrupted arterial flow and testicular pain. If blood flow to testis is absent for 4 to 6 h, spermatogenesis may be permanently lost. Code History. 2016 (effective 10/1/2015): New code (first year of non-draft ICD-10-CM) 2017 (effective 10/1/2016 .Testicular torsion causes severe testicular pain and usually occurs in boys 10 years and older. While it generally occurs in adolescent boys, it may also occur during fetal development or shortly after a baby is born. Causes. In pre-adolescent and adolescent boys, torsion occurs primarily from incomplete attachment of the testes within the scrotum.
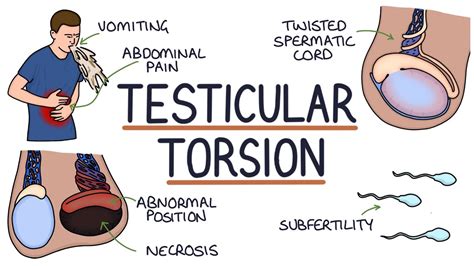
In one retrospective review of 100 boys younger than 15 years who presented to the emergency department with acute testicular pain, researchers found that 70 had torsion of the appendix testis, 12 .Testicular torsion is a medical emergency. It happens when the spermatic cord, which provides blood flow to the testicle, rotates and becomes twisted. This cuts off the testicle's blood supply and causes sudden pain and swelling. Testicular torsion usually needs immediate surgery to .
INTRODUCTION. Representing approximately 8% of all visits, abdominal pain is the most common complaint encountered in the emergency department (ED).1 While the etiology may vary, genitourinary sources of pain must be considered including testicular torsion. Although testicular torsion frequently presents as acute scrotal pain, torsion of an .
how to identify testicular torsion
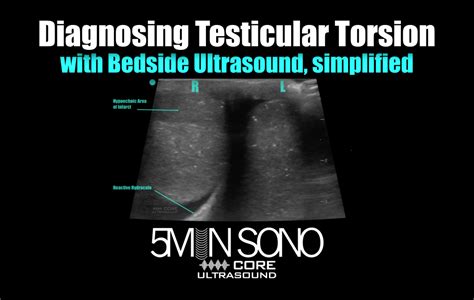
The spermatic cord provides blood flow to the testicle. Testicular torsion is when a testicle rotates on this cord. It can lead to pain, swelling, and other symptoms and needs urgent medical . The Prehn sign is not reliable for predicting torsion (relief of pain with testicle elevation). Torsion of the testicular appendages is more common and not dangerous. During early onset, this may be differentiated from testicular torsion by maximal tenderness to palpation near the head of the epididymis or testis, an isolated tender nodule, and .
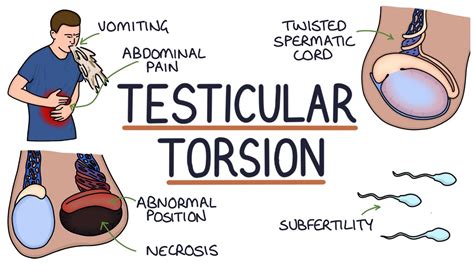
Testicular torsion is a urological emergency caused by the loss of testicular tissue due to ischemic damage. Rapid diagnosis and urgent treatment play a crucial role in the management of testicular torsion. Manual detorsion can be performed at the bedside, thereby reducing the duration of ischemia. Recent studies have reported the use of point-of-care ultrasonography .Introduction: A myriad of pathologies can cause abdominal pain. Genitourinary causes including testicular torsion must be considered. Case report: In this report, we present a 17-year-old male evaluated in the emergency department for lower abdominal pain. After physical exam, computed tomography, and ultrasound were completed, torsion of undescended testicle within the .
2 Contents 1 Foreword 2 2 Summary of key pathway components 3 3 Testicular torsion pathway 3 3.1 Raising awareness 4 3.2 Referral pathways 4 3.3 Assessment, including TWIST score & ultrasound 5 3.4 Surgery 6 3.5 Follow up 6 3.6 Revalidation & maintaining skills 6 4 Patient experience 7 5 Audit points & areas for further research 8 6 Resources & further information 8
acute testicular pain (N = 187) underwent surgical explora-tion, torsion of the appendix testis accounted for 56% of all . examination sign for diagnosing testicular torsion [10].A positive or normal cremasteric reflex is seen when the testicle retracts after light stroking of .ICD 10 code for Torsion of testis, unspecified. Get free rules, notes, crosswalks, synonyms, history for ICD-10 code N44.00. . It manifests with acute testicular pain. If immediate medical assistance is not provided, it will lead to necrosis and loss of the testicular tissue. . 2016 (effective 10/1/2015): New code (first year of non-draft .That denial comes at a cost. If the torsion isn't corrected quickly, the testicle may die. 30-40% of cases of testicular torsion results in loss of the testicle. What are Symptoms of Testicular Torsion? The symptoms of testicular torsion may involve one or both of the testes. The following are the most common symptoms of testicular torsion.
uncertainty for brix refractometer
uses for brix refractometer
Name: Sweetie Fox . Height: 5′ 4″ Weight: 141 lbs . Body measurements: 36-26-46 Inches. Hair Color: Vixen Brunette . Eye Color: Brown/Blue . Tattoos: Never. Hey, guys! Great to see you in my official fan club. Since you're here, you probably know about me, but let's get to know each other better🥰 . I have a lot of passions in my life.
1 to 10 pain of torsion of testes|can you fix testicular torsion yourself